Biodiversity
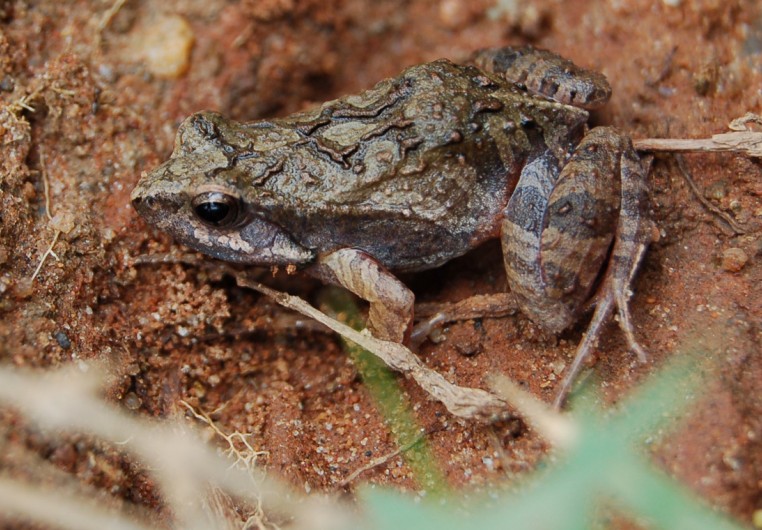
 Barker Frog
Physalaemus cuvieri | Fitzinger, 1826
Barker Frog
Physalaemus cuvieri | Fitzinger, 1826

Vocalization

Characteristics: Small to medium-size species measuring about 2.0cm to 3.5cm in length. Its back can be dark with weak shades of brown, gray or even green with spots or irregular stripes. Most individuals have the inner thighs and inguinal areas in colors ranging from orangish to reddish. Its belly is white, spotted dark on the chest and throat. Males are slightly smaller than females and have a darker neck. Its song resembles a bark, giving it its popular barker frog name.
Distribution: It is widely distributed, occurring in the North, Northeast, Midwest, Southeast and South of Brazil, Argentina, eastern Paraguay, and Bolivia.
Habitat: Open formations, in savannas and scrublands to forest formations in riparian and gallery forest edges, lakes, ponds, wetlands, swamps, rivers and lentic streams, and in permanent and temporary ponds.
Habits: Crepuscular, nocturnal, terrestrial, and aquatic. It prefers low vegetation (grasses) near streams and puddles of water. It can be found during the day sheltered on logs and rocks, in open areas and forest edges.
Diet: This frog feed on small spiders and millipedes, although they have a preference for small insects and beetle larvae.
Breeding: Oviparous, this species' reproductive period is restricted to rainy periods. Males vocalize in permanent or temporary environments, from the ground in still water swampy areas. Females may spawn twice per season, laying 400 to 700 eggs into white foam nests that either float or are partially attached to the ground or grasses.
UFRA: Species seen in Organic sugarcane fields, Wetlands with herbaceous plants, Wetlands with riparian forests, Restored native forests, and Drainage Ditches.